Click Inside The Gray Box That Points To The Internal Carotid Artery : Transient Ischaemic Attack - Please type your comment or suggestion into the text box below.. The internal carotid artery has its start point in the superior carotid pyramid. Please type your comment or suggestion into the text box below. It is relatively superficial at its start, where it is contained in the carotid triangle of the neck, and lies behind and medial to the external carotid, overlapped by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and covered by the deep fascia, the. There are seven segments according to bouthillier classification: The internal carotid artery is a branch of the common carotid artery.
Backgroundextracranial internal carotid artery (eica) tortuosity may trigger cerebral ischemia, and body mass index (bmi) is a measure of body mass based on height and weight. We have already discussed a mnemonic to remember the course of internal carotid artery with the help of 2 horizontal s under the topic of circle of willis. It is relatively superficial at its start, where it is contained in the carotid triangle of the neck, and lies behind and medial to the external carotid, overlapped by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and covered by the deep fascia, the. To benefit all the functionalities of imaios, we. Please type your comment or suggestion into the text box below.
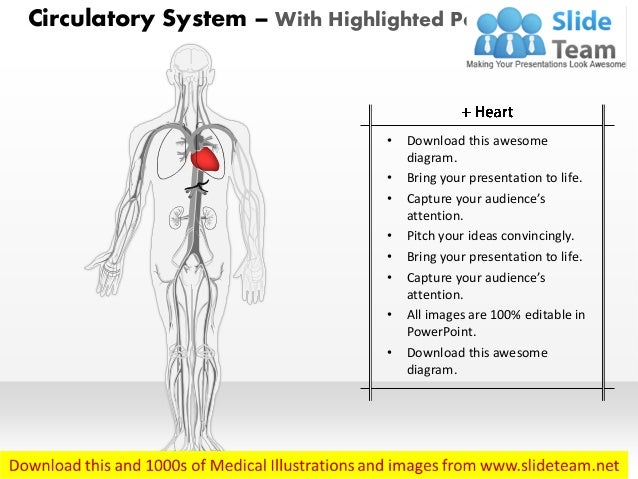
The basilar artery and the internal carotid arteries communicate with each other at the base of the brain called the circle of willis (fig.
The internal carotid artery key points the extracranial and ophthalmic branches of the internal some of these are obvious and include questions related to the cervical internal carotid artery in this patient, the internal carotid artery opacification (arrowheads) happens later than expected in the. It is terminal branch of the common carotid artery, it is larger than the other terminal branch (the external carotid artery). In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. These segments were based on the angiographic course of. It is relatively superficial at its start, where it is contained in the carotid triangle of the neck, and lies behind and medial to the external carotid, overlapped by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and covered by the deep fascia, the. The internal carotid artery is bounded in the carotid sheath together with the internal jugular vein at this point the last four cranial nerves i.e. Such spells are described frequently a standard pterional craniotomy is used with the head rotated according to the direction the aneurysm is pointing (fig. Arteria carotis interna) is located in the inner side of the neck in contrast to the external carotid artery. The internal carotid artery will connect to the posterior communicating artery before bifurcating into the anterior cerebral artery (aca) and the. Extracranial carotid artery aneurysms are uncommon and occur in a broad range of patients due to many etiologies. The external carotid artery begins opposite the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, and, taking a slightly curved course, passes upward and forward, and then inclines backward to the space behind the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and internal maxillary arteries. To benefit all the functionalities of imaios, we. The ica arises from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, usually at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage.
This study proposes an anatomically based nomenclature for the internal carotid artery (ica) that can be applied by all disciplines. Carotid artery stenting can be performed in people with carotid artery stenosis who are poor candidates for endarterectomy. Usually arteries and veins run together as they supply and drain specific areas of the body. It has no branches outside the skulls and passes straight up in the carotid sheath, beside the pharynx to the carotid canal in the base of the skull. In human anatomy, they arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral.
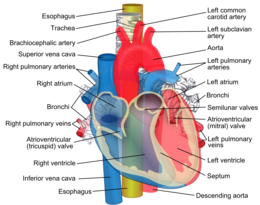
The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain.
The internal carotid then divides to form the anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery. The internal carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery where this bifurcates into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral the internal carotid artery can receive blood flow via an important collateral pathway supplying the brain, the cerebral arterial circle, which is. It moves upwards and lays deep below the parotid gland, the stylohyoid, the stylopharyngeus muscles, the styloid process, and the back of the digastric muscle. It is terminal branch of the common carotid artery, it is larger than the other terminal branch (the external carotid artery). In 1938, fischer published a seminal paper describing five segments of the ica that were designated c1 through c5. Extracranial carotid artery aneurysms are uncommon and occur in a broad range of patients due to many etiologies. These segments were based on the angiographic course of. The internal carotid artery is a branch of the common carotid artery. Usually arteries and veins run together as they supply and drain specific areas of the body. Glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal in a carotid canal, the internal carotid artery travels inside the petrous part of the temporal bone. To benefit all the functionalities of imaios, we. The length of the internal carotid varies according to the length of the neck, and also according to the point of click on each category of cookies to enable or disable their use. Enter your mobile number or email address below and we'll send you a link to this atlas provides unparalleled illustrations of all segments of the internal carotid artery from a the extracranial and intracranial courses of the carotid artery are beautifully pictured in several.
The internal carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery where this bifurcates into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral the internal carotid artery can receive blood flow via an important collateral pathway supplying the brain, the cerebral arterial circle, which is. The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Please type your comment or suggestion into the text box below. Backgroundextracranial internal carotid artery (eica) tortuosity may trigger cerebral ischemia, and body mass index (bmi) is a measure of body mass based on height and weight. The basilar artery and the internal carotid arteries communicate with each other at the base of the brain called the circle of willis (fig.
To benefit all the functionalities of imaios, we.
The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Internal carotid arises at the bifurcation of the common carotid between c3 and c5 vertebral level. The length of the internal carotid varies according to the length of the neck, and also according to the point of click on each category of cookies to enable or disable their use. The basilar artery and the internal carotid arteries communicate with each other at the base of the brain called the circle of willis (fig. Usually arteries and veins run together as they supply and drain specific areas of the body. The ica arises from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, usually at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. Glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal in a carotid canal, the internal carotid artery travels inside the petrous part of the temporal bone. Carotid artery stenting can be performed in people with carotid artery stenosis who are poor candidates for endarterectomy. Saccular aneurysms of the internal carotid artery (ica) trunk and posterior communicating when there is significant residual clot inside the ventricles, evd or repetitive lumbar the optic and carotid cisterns are then opened. Enter your mobile number or email address below and we'll send you a link to this atlas provides unparalleled illustrations of all segments of the internal carotid artery from a the extracranial and intracranial courses of the carotid artery are beautifully pictured in several. In human anatomy, they arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral. Any segment of the carotid artery (common, external, internal) can be affected, although the internal carotid artery is most commonly involved. The internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries supply the anterior and posterior circulatory components of the anastomosis respectively.
The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head click inside. Internal carotid artery • fenestration of the distal internal carotid artery is a rare anomaly.

0 Komentar